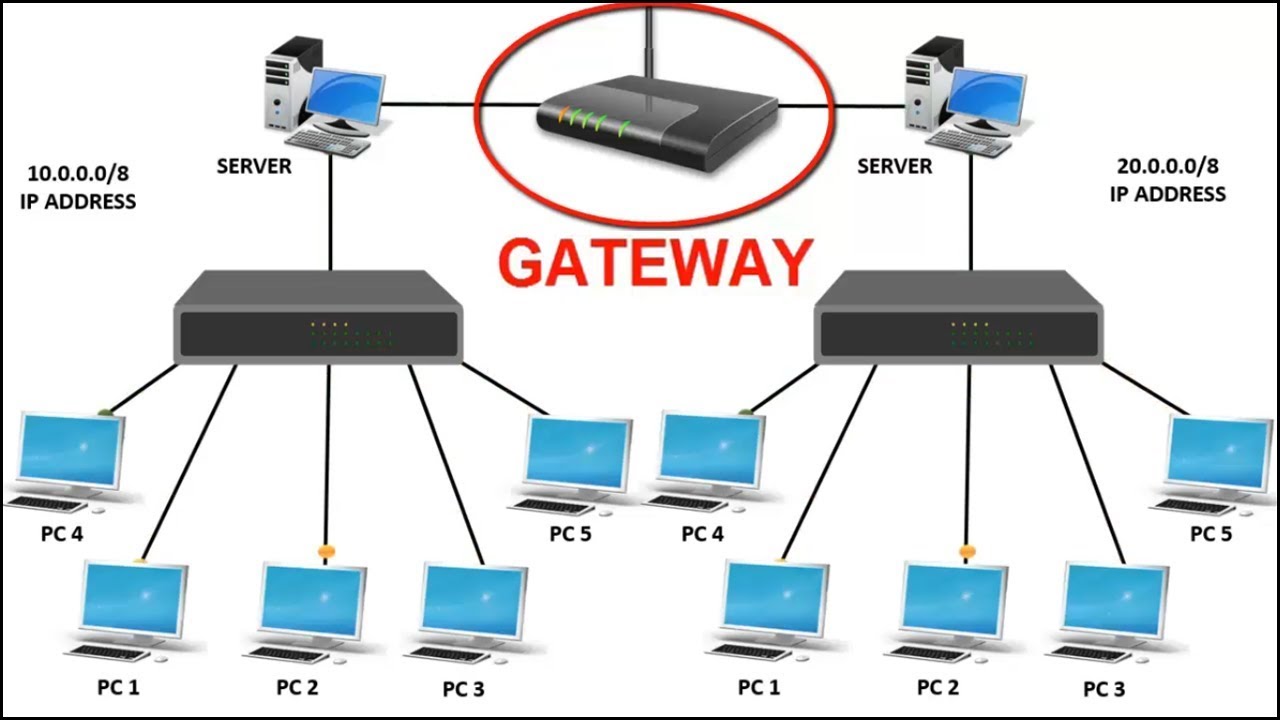
Gateways: In the vast expanse of the internet, where data traverses countless networks to reach its destination, gateways play a pivotal role. But what exactly is a gateway, and why is it crucial for modern networking? Let’s delve into the fundamentals to demystify this integral component of network infrastructure.
What is a Gateway?
In simple terms, a gateway is a node or a device on a network that serves as an entry or exit point for data. It acts as a bridge between different networks, facilitating communication by interpreting and translating data between incompatible systems or protocols. Essentially, a gateway enables seamless connectivity between disparate networks, allowing them to exchange information efficiently.
Types of Gateways
Gateways come in various forms, each serving specific purposes based on the networks they connect and the tasks they perform:
- Network Gateways: These gateways connect networks using different communication protocols. For instance, a network gateway may translate data between a local area network (LAN) and the internet, facilitating communication between devices within the LAN and external networks.
- Protocol Gateways: Protocol gateways translate data between different network protocols, such as TCP/IP, UDP, HTTP, and FTP. They ensure compatibility between devices or networks that use different communication protocols, enabling seamless data exchange.
- Application Gateways: Application gateways, also known as application-level gateways or proxy servers, operate at the application layer of the OSI model. They provide security and protocol translation services for specific applications, such as web browsing, email, and file transfer. Application gateways often include features like firewall protection and content filtering.
- VoIP Gateways: Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) gateways convert voice signals from traditional telephone networks into digital data packets for transmission over IP-based networks. They bridge the gap between traditional telephone systems and modern IP-based communication networks, facilitating seamless voice communication over the internet.
Functions of Gateways
Gateways perform several essential functions that enable communication between networks and devices:
- Protocol Translation: Gateways translate data between different network protocols, ensuring compatibility between disparate systems.
- Address Translation: Gateways may perform network address translation (NAT), translating IP addresses between private and public networks to enable communication across the internet.
- Routing: Gateways make routing decisions, determining the most efficient path for data to travel between source and destination networks.
- Security Enforcement: Many gateways incorporate security features such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption to protect networks from unauthorized access and malicious activities.
- Performance Optimization: Gateways may optimize network performance by caching frequently accessed data, compressing data for faster transmission, or prioritizing traffic based on predefined criteria.
Importance of Gateways in Networking
Gateways play a critical role in enabling seamless communication and connectivity in modern networking environments. Some key reasons why gateways are essential include:
- Interoperability: Gateways enable interoperability between networks and devices with different protocols and standards, facilitating communication and data exchange on a global scale.
- Security: Gateways serve as a frontline defense against cyber threats by enforcing security policies, filtering malicious traffic, and monitoring network activity for suspicious behavior.
- Scalability: Gateways allow networks to scale efficiently by providing routing and translation services that accommodate the growth of connected devices and expanding network infrastructure.
- Flexibility: Gateways offer flexibility in network design and architecture, allowing organizations to integrate diverse technologies and adapt to evolving business requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gateways play a fundamental role in modern networking by facilitating communication between disparate networks, protocols, and devices. Whether connecting local networks to the internet, translating data between different protocols, or ensuring security and performance optimization, gateways are indispensable components of network infrastructure. Understanding the functions and importance of gateways is crucial for building robust and interconnected networks that meet the demands of today’s digital world.